Lots of digital marketers say there’s too much competition for ecommerce SEO these days.
But that’s not true. There is plenty of ecommerce SEO strategy that you can follow to get your product detail pages to the top of the search results (if you want to be a part of the 23.6% of ecommerce orders that come from organic traffic, that is).
In this guide, I’ll show you how to link your SEO and ecommerce, ultimately increasing sales and helping your site live up to its potential.
This article outlines nine essential steps to successful ecommerce SEO:
- Do dynamic optimization
- Practice internal linking
- Develop your website architecture
- Fix technical SEO issues
- Create ecommerce content
- Perform keyword research
- Block bad links
- Create a review generation strategy
- Use schema markup
- Build a brand
- Practice distributed ecommerce
1. Do Dynamic Optimization
This isn’t an option. You must practice dynamic optimization if you want your site to rank.
If you’re unfamiliar with dynamic optimization, it’s a means of optimizing dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of pages all at once.
How do you do that? With the aid of a template.
Each page displays content based on a template. When you update the template, you’re updating all the pages that use the template at once.
It’s not only a time-saver, it can also land your website at the top of the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Let’s say you’re selling baseball caps online. You offer caps with different sizes and colors.
Obviously, you’d want category pages that represent all possible combinations. For example, you’d want a category page for “red XL baseball caps” and another category page for “blue small baseball caps.”
Now, you could create all of the category pages manually. But then you’d have to do that for each size/color combination.
That’s not efficient.
On the other hand, if you use a template, you could create a template with a title like “(color) (size) Baseball Caps.”
Then, you’d just substitute different colors and sizes at the appropriate place in the title.
Obviously, the category page itself would only show baseball caps that match the criteria in the title.
That’s a simplistic example of dynamic optimization. But it gives you an idea of how you can use it to generate lots of optimized web pages with very little effort.
Keep in mind: you don’t just optimize the title with dynamic optimization, either. You also optimize the H1 tags, image tags, and content. It’s a great way to create thousands of unique pages on the fly.
You’ll also find that dynamic optimization will increase your click-through rate (CTR) and overall conversions in addition to improving your exposure in the search results.
Final note: once you’ve rolled out your dynamic optimization strategy, make sure you test it.
For example, if you find that you’ve updated a thousand pages for one template and it increased the CTR by a percentage point, you should probably roll out the change you made on that template to other templates.
On the other hand, if you find that a change you made to just one template decreased your engagements, consider rolling that change back.
2. Practice Internal Linking for Ecommerce SEO
The easiest links you’ll ever get to your website will come from your own website. Unfortunately, many SEOs still fail to practice good internal linking strategies.
That’s especially true when it comes to ecommerce SEO.
For starters, make sure that you’re linking from the home page. That’s a great way to increase the prestige of some of your more important pages.
Also, link to your own site from your global header and footer.
If you’re running a website that’s similar to most, you’ll likely use the same header and footer for all your pages. Use that digital real estate to link to important pages on your site.
Additionally, go with a shallow linking strategy. In other words, make sure Googlebot can get to any page on your site quickly.
If it takes Google 17 jumps to get to a product detail page, it’s not likely that page will get a very high rank.
Next, avoid putting more than 200-300 links on a single page.
Why? Because if you have too many links on one page, Google tends to devalue the links.
Learn the art of page-sculpting. That’s a strategy that digital marketers use to place internal links on pages so they earn the proper link weight.
If you get too conservative with your page-sculpting, you’ll end up with too many pages. If you get too liberal, you’ll end up with too many links on a single page.
It’s important to strike just the right balance.
Next, you should also link to all your subcategories within each category page. That’s one way to make sure that Google finds all your products and their associated categories.
Also, if you have copy on a category page, make sure to internally link to other categories at the same level. Link to product pages as well, but only lower in the copy.
Finally, put links on product detail pages as well. Beyond adding related product links, also link to similar categories and subcategories.
3. Develop Your Website Architecture
So you run an ecommerce site. Then you ought to know better than anyone why it’s crucial to develop a website architecture, if only to organize your extensive list of pages.
As you develop your website architecture, keep these two things in mind:
- Simplify your architecture as much as possible. This makes it way easier for you scale when the time comes.
- Try to keep every page just three clicks (or less) away from the home page.
Any ol’ site structure won’t do. Here’s what you should stay away from:
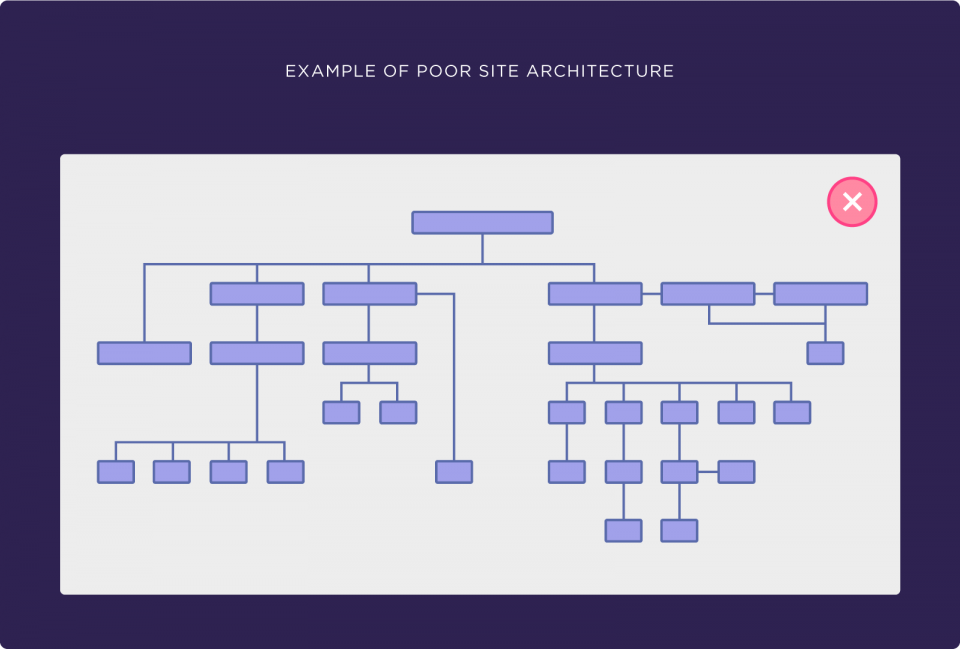
Image source: Backlinko
You can tell that this architecture is disorganized and not the most user friendly out there. On the contrary, something like this is a good vision to strive for:
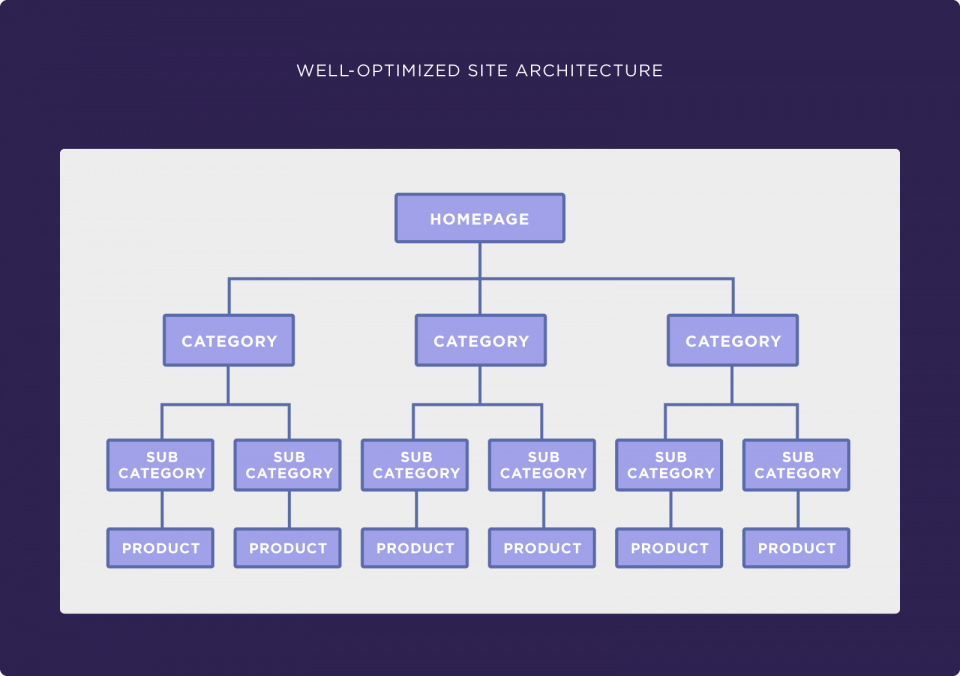
Image source: Backlinko
Here, the organization is way more structured, which will inevitably improve SEO for ecommerce website functioning.
4. Fix Technical SEO Issues as Part of Your Ecommerce SEO Strategy
Unfortunately, plenty of ecommerce websites have technical SEO issues. If yours is one of them, fix those problems today.
There are a few ways to do this, but first, I want to emphasize something. Technical SEO is extra crucial for companies looking to enhance their ecommerce SEO strategy. Why? Because online stores rely on searchability, and they often have a ton of pages to index due to their varied products. As a result, technical SEO for each of those pages needs to be in sync, so it’s really not something you can skimp on.
First, make sure your search pages are blocked so they don’t get picked up by Google.
Your website probably includes a search bar that appears on every page. Visitors can type keywords into the search bar and look for items of interest.
The problem is that the search usually generates a unique URL with request parameters. Make sure the URL is blocked in your robots.txt file.
Likewise, ensure that your faceted navigation is blocked.
If you’re unfamiliar with faceted navigation, it’s a feature that you (probably) have on your website that enables visitors to filter their results based on price, color, size, etc.
Again, that kind of navigation uses a URL that you want blocked to the search spiders. Those pages shouldn’t get indexed.
Be careful with pagination as well. Google has already deprecated the use of rel/next and rel/prev, so if you’re still using those tags, get rid of them.
Also, infinite scrollers might pose a problem with ecommerce SEO. Those are web pages that keep “expanding” vertically as the visitor scrolls down.
The issue with those pages is that some search bots might have trouble with the scrolling part. So they can’t traverse links that appear only after scrolling.
Next, make sure you’re using sitemaps.
Remember, though, sitemaps can only contain a maximum of 50,000 URLs.. If you have more than 50,000 URLs you need to index, use sitemap indexes.

XML sitemap for ecommerce SEO image source: Practice Ecommerce
Finally, avoid product level duplicate content.
It’s easy to include duplicate content on an ecommerce website. In fact, you may already have it if you just copied and pasted the product descriptions from the manufacturer.
The problem is that many other ecommerce site webmasters who are selling the same products copy the descriptions as well. As a result. you’ve got the same content on your website that’s on dozens of other sites.
That’s duplicate content. And it will make it difficult to rank your ecommerce website.
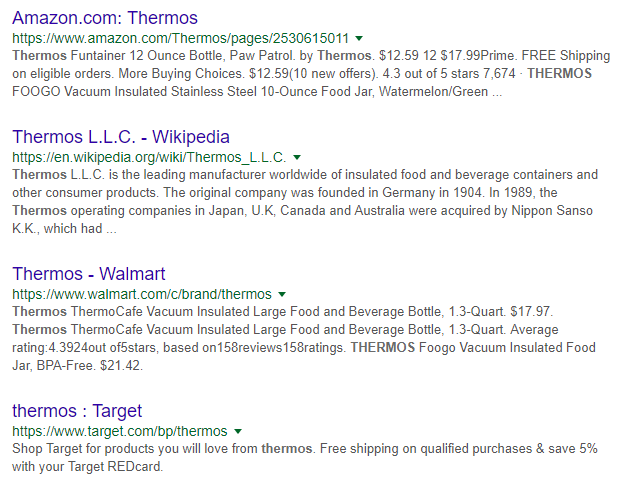
Duplicate content ecommerce SEO strategy image source: Neil Patel
Also, when you have different product detail pages for the same product with different attributes, you’ll often publish duplicate content as well.
For example, if your description for a blue baseball cap is the same as your description for a red baseball cap but they both appear on different pages, you’ve got duplicate content.
5. Create Ecommerce Content
Yes, you need to do content marketing with ecommerce sites. That’s in addition to your ecommerce SEO.
Why? Because it will attract more people to your site.

Image Source: Angie’s List home improvement content page
Be careful with content marketing, though. You don’t want to optimize your content for keywords that should lead people to your ecommerce product detail pages.
For example, the keyword “blue XL baseball caps” should point to a category page or a product detail page. If you write an article optimized for “blue XL baseball caps,” you’ll take visitors away from the ecommerce side of the site.
That could lower your sales.
Also, some strategists create too many categories. If you do that, you’ll end up with thin content.
Google doesn’t like to rank thin content towards the top of the SERPs.
You should also include content on your category pages. That gives Google more insight about the kinds of products within that category.
Be careful with putting too much content on the cat pages, though. If you write an article on a category page, Google will treat the page as… an article.
Include details on your product pages for ecommerce SEO, but not so much that it looks like an article.
In other words, it won’t get ranked as a category page on an ecommerce site. That could hurt your sales as well.
For more on this, I wrote a full guide on ecommerce copywriting. Check it out here.
6. Perform Keyword Research for the Ultimate SEO and Ecommerce Synergy
Keyword research is at the root of your ecommerce SEO strategy. Really.
Since your customers are going to be people searching for products, you’ll want to focus on product searches the most. This is different from navigational queries and informational searches, for example.
Amazon’s suggested searches is a helpful tool for ecommerce keyword research. It’s quite manual, but it makes sense considering how successful they are in the ecommerce realm. Type up to three words in the search bar and collect the suggestions that drop down.
You can also view Amazon and other competitor sites to analyze their categories for keyword research.
Other options include the Keyword Tool Dominator (free), Google Keyword Planner (free) and Wikipedia (also free!).

Ecommerce keyword research on Wikipedia
Of course, paid tools like SEMRush will surely not disappoint you.
7. Block Bad Links for Ecommerce SEO
It’s still a great idea to block bad links.
That’s true even if you didn’t solicit the bad links. Google might think you’re practicing some kind of link spam and penalize your site accordingly.
How do you block bad links? With the disavow tool.
Fortunately, it’s easy to use. You can access it from within Google Search Console.
Keep in mind: blocking bad links isn’t a one-and-done process. You’ll need to do it on a bi-weekly or monthly basis.
If you let it go, you could wake up one day with a nightmare on your hands when you find Google has penalized your site because of link spam.
And while we’re talking about links, you should not only block the bad links, but you should also aggressively pursue good links as well.
Ecommerce sites need a healthy backlink profile just like traditional info sites.
8. Create a Review Generation Strategy
When you’re shopping online and see a product you’d like to buy, what do you normally do?
If you’re like many other people, you’ll check the price, take a look at the image from different angles, read the product description, and… check the reviews.
You’ll almost always check the reviews, won’t you?
Your website visitors are no different than you are when it comes to shopping online. They want to see positive reviews.
That’s why you should pursue a review generation strategy that lets people know your products have delivered for other customers in the past.
Also: the more positive reviews you generate that are unique, the more likely you’ll get a good rank in the search engines.
As for how you ask for those reviews, there are a few strategies you can try, but emails are a good place to start for ecommerce SEO.
This doesn’t have to be an extravagant ask. After a customer makes a purchase, follow up a few days later via email to ask how they’re liking the product, if they have any questions, and, if satisfied, to kindly leave a review or star rating.
Simple, straightforward, and to the point.
Even better, the process can be automated through the use of tools like Shopper Approved and BirdEye.
9. Use Schema Markup to Boost SEO for Ecommerce Websites
One of the best ways to outrank your competitors is to use technology that Google loves but that others aren’t using. One of those technologies might be schema markup.
If you’re unfamiliar with schema markup, it’s a library of tags you can use to tell the search engines a little bit more about the content on your page. It’s especially useful for ecommerce SEO.
For starters, you should use the review markup. It will highlight your reviews for the search engines.
Ecommerce SEO strategy schema review markup image source: Moz
And if you want to know why that’s important, see Point #6 above.
Beyond that, though, you should also use the logo markup (to promote your brand) and breadcrumb markup (for navigation).
Finally, you should use the product markup on your product detail pages.
10. Build a Brand
It’s not enough to just publish product detail pages and optimize a site for ecommerce content. You’ll need to build your brand as well. That means you’ll need to invest some money in advertising.
Keep in mind, that’s not just advertising for specific products (although that has a place, too). You should run ads that promote your business as well.
Inform people about your brand and tell them why they should buy from you.
Additionally, do some PR.

Benefits of PR for ecommerce SEO strategy
Since plenty of ecommerce sites aren’t investing any time or money in PR, you might find that doing so gives you a competitive advantage.
11. Practice Distributed Ecommerce
Okay, you have a great website. Is that the only place online where people can find your products?
If so, consider expanding.
You can sell products on websites hosted by Amazon, Walmart, Target, and others. You don’t need to confine your marketing to your own virtual shop.
Sure, those other sites will take a piece of the pie. But in the process of marketing through other channels, you’ll promote your brand.
So you’re selling something and getting the word out about your business at the same time. What’s not to love about that?
Wrapping Up Our Rundown of Ecommerce SEO Strategy
There you have it. Follow the steps listed above and you’ll push your SEO for ecommerce website optimization to the limit.
Remember, though: always be on the lookout for new ways to gain exposure. Although these steps are a great starting point, you’ll have to build on them later on.
