Every year, more brands are discovering Podcasting’s ability to expand their reach. It’s a launchpad for building loyal fans, getting content ideas, and becoming a thought leader.
So in this article, you’ll learn how to make a podcast for your business. You’ll learn what podcasts are, why you should make one, and how to do it.
Plus, we’ll teach you to optimize your podcast for search and build organic listeners.
What You’ll Learn:
- The Rise of Podcasts
- Why You Should Integrate Podcasts into Your Content Strategy
- Breaking Down Perceived Barriers to Entry
- Starting Your Podcast
- How to Optimize Your Podcast for Search Engines
- How to Find Podcast Guests
- How to Monetize Your Podcast
The Rise of Podcasts
Podcasts continue to grow nonstop. According to estimates, 100M Americans will listen to podcasts by 2024—up 24M from 2020.
And as Google Trends data shows, interest in “podcasts” has steadily risen since a BBC journalist coined the term in 2004.
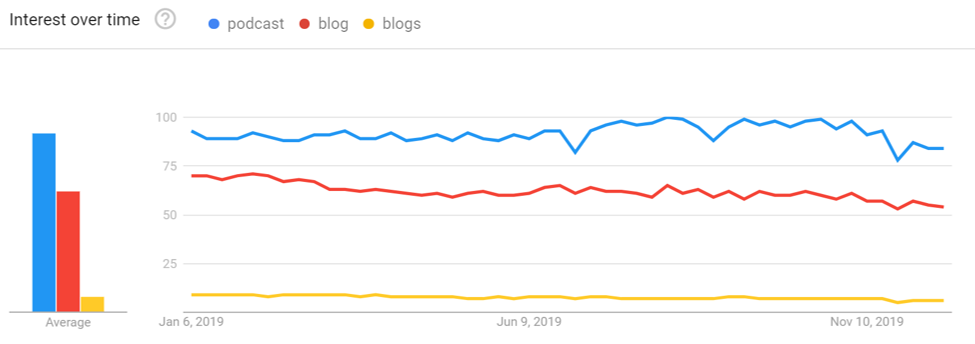
Searches for podcasts have increased, according to Google Trends
Podcasting is here to stay, just like radio, TV, and the Internet. Investing in a podcast now means getting there early.
What Are Podcasts?
A podcast is an audio program that consists of one or more episodes, much like traditional talk radio.
Podcasts aren’t an entirely new idea. After all, people have listened to radio programs for almost 100 years. The major difference is listeners can stream their favorite episodes on demand.
Podcast topics cover everything from informational news updates and serial journalism to fictional episodes, celebrity interviews, and comedy of all flavors.
While you might think of podcasts as an entertainment platform or a news source, the beauty of this format is that it works for just about any topic—whether you’re all about personal growth or want to take in the history of the Earth one download at a time.
The majority of podcasts are an audio-only experience; however, video podcasts do exist.
That said, if you’re creating a podcast, you’ll likely be better off sticking with convention.
Part of the appeal of podcasting is that it’s a medium that can inform or entertain, while at the same time functioning as background noise.
Why You Should Integrate Podcasts into Your Content Strategy
Podcasting has several advantages over other media channels:
Fast & Inexpensive Way to Create Content
At its core, podcasting is recording a conversation. It gets more complex than that, but the overall process is simpler than content writing or video editing.
Sure, quality studio equipment gets expensive. But starting out, a $50 studio mic, a laptop, and conversational skills are all you need.
Optimal for Connecting with Experts
Podcast interviews are one of the best ways to recruit experts and get their honest, in-depth insight. Unlike written posts or video interviews, podcasts need little work from guests—they just need to call in and talk about something they’ve done before.
Also, starring in a podcast often represents a career opportunity for guests. A prominent display of their expertise helps establish their authority.
High Listener Loyalty
Thanks to podcasting’s 1:1 structure, hosts have a unique ability to build relationships with their audiences. Like with any other person, listeners come to understand their thought process, sense of humor, and expertise.
In other words, the host essentially becomes the listener’s friend.
That’s why listeners tend to stick with a great host once they find one. This host becomes their go-to for long drives, morning coffee, and background listening.
Improved Branded Search Performance
When someone Googles your company name, it’s crucial your channels occupy each space on page one. Competitors can seize your organic interest by making content about your brand if you don’t.
And since you’ll host your podcast on a third-party platform, it will appear separately from your website (like your social profiles). Even better, you’ll build EAT with Google thanks to the expanded search presence.
Great for Building Brand Authority
Creating content for a single channel (blogging, YouTube, etc.) can lead to uneven brand authority. Instead of an industry leader, people will just see you as another blogger or Youtuber.
Branching out into podcasting helps diversify your brand’s strength in a big way. By interacting in multiple spaces, your brand becomes an all-encompassing thought leader.
That’s why Blue Apron hosts a podcast about the psychology behind food trends. Now they’re not just a meal kit company—they’re a culinary thought leader.
Richer Search Presence
Since May 2019, Google has been indexing podcasts in search results.
So if your competitors already rank for your target keywords, jumping on the podcast wagon can help you gain a competitive edge by being one of the first to optimize your podcasts.
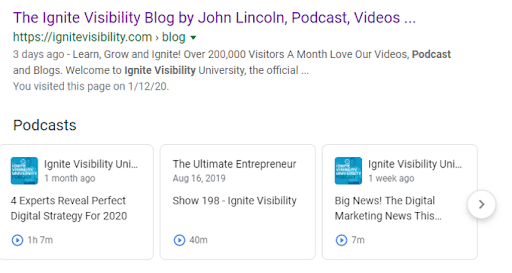
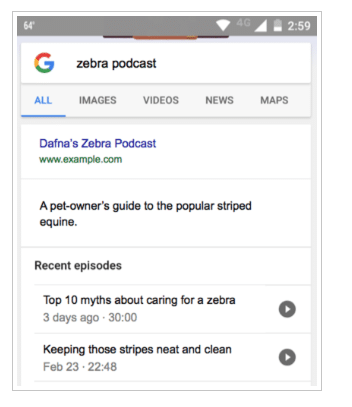
In the example below, you can see how the Ignite Visibility podcasts appear in the SERPs. They stand out a lot more than the link to the blog that appears above them, right?
Breaking Down Perceived Barriers to Entry
Odds are you already have everything you need to podcast. But most people don’t know this and think podcasting belongs only to a certain group of experts.
Here are the biggest myths stopping people from starting a podcast:
“I need a specific skill set”
You only need two skills to start a podcast:
- The ability to speak
- Passion about a certain subject
You don’t need to be an expert either. As long as you care enough about something to discuss and research it passionately, you have all the skills you need.
“I need expensive equipment”
A microphone and a laptop (for editing and uploading) are all you need to start a podcast. While you’ll grow into better tools later on, the basics will serve you fine starting out.
“Podcasts are dying out”
If podcasts were dying out, brands like Apple and Spotify wouldn’t invest billions of dollars into it. They’ll be around for decades to come—if not centuries.
“I need an established following”
A new podcaster’s biggest fear is speaking to crickets. And this fear isn’t necessarily misplaced—listeners are never guaranteed.
That said, consistently creating quality content is a reliable path to success. You shouldn’t be afraid of this as long as you provide genuine value to people (and can spend years building an audience).
“I need to plan out long episodes”
Podcasts don’t have a set length—it all comes down to you and your audience. Some shows run for 30 minutes, others for three hours.
That said, keeping length consistent is key. Every episode should be the same lengths so your audience knows what to expect from you.
Starting Your Podcast
With a little effort, you can launch your podcast in a week’s time. Here’s how to get started:
1. Find a Niche
All meaningful content starts with a defined niche.
Focusing on one topic lets you build true fans who follow your insight on a topic you’re passionate about. That said, it should still be broad enough that you have plenty of content to cover.
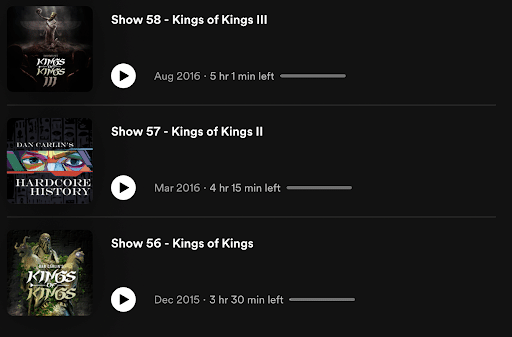
For example, Dan Carlin’s Hardcore History podcast covers various historical periods. It’s niche enough to build a large following of history enthusiasts, yet broad enough to never run out of fresh material.

Dan Carlin’s Hardcore History
2. Define Your Audience
Before doing anything else, think about the typical person your podcast will appeal to. This enables you to create content that’s valuable and relevant to their interests.
Get some basic demographic info about your ideal listener, like:
- Age
- Location
- Occupation
- Hobbies
- Common problems they face
- Information they want to learn more about
3. Choose a Name
Your podcast’s name should be a clever signal to your subject matter. Keep it short and concise to keep it memorable and easy to include in promotional materials.
Here are examples of real podcast names and the topics they cover:
- Extra Napkins, food comedy
- The School of Greatness, self improvement
- Unlocking Us, stories about human emotion
- Philosophize This!, philosophy
Also, avoid using “podcast” in your name since it’s redundant (people will know it’s a podcast).
4. Create Cover Art
You’ll need cover art for your podcast’s main cover. You can create cover art for each individual episode (think of this as a way to help you stand out).
You can make this art as simple or complex as you like. It just needs to clearly signal the name of your podcast and preview its content.
For instance, Dan Carlin uses unique illustrations to signal the quality and uniqueness of each episode:
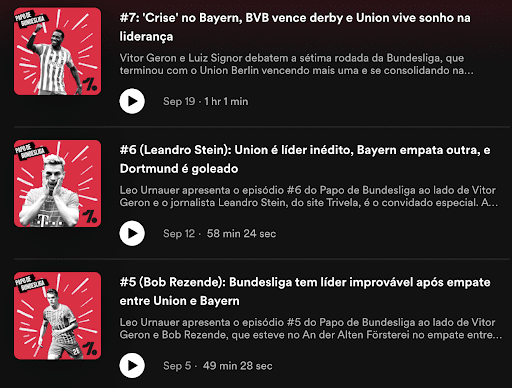
But you don’t need to make it that artistic. You can use more basic art, like this soccer podcast:
5. Make a Publishing Schedule
An important part of building a following is having a consistent publishing schedule. It doesn’t need to be every week or even every month, but it does need to be steady.
Without a schedule, your followers won’t know when to expect your podcast. They’ll only see it whenever they happen to check your profile.
6. Keep Length Consistent
Episodes should have roughly the same runtime. If you keep length consistent, you’ll build followers who tune in specifically because of it.
For example, Dan Carlin’s listeners tune in for an hours-long study into a historical period. But soccer podcast listeners might tune in for a 15-minute recap of last week’s games.
7. Consider a Co-Host
Having a co-host on your podcast helps for several reasons:
- Help with writing the script
- Having someone to bounce ideas off
- Offloads some of the talking for long shows
- Builds chemistry that listeners find captivating
You can find co-hosts in your personal network, forums in your niche, posting job offers, or asking guests to join you permanently.
8. Select Your Tools
You can start your podcast with a laptop and a basic microphone.
But if you have the budget for it, better equipment can make your podcast seem more professional. Decent podcast microphones give your show a much crisper sound, and start at around $100.
As for editing software, free tools like GarageBand and Audacity work fine. That said, premium tools like Adobe Audition can make editing easier and higher quality.
9. Build Your Online Presence
Almost all popular podcasts have a large online presence to maximize their reach. You don’t have to replicate their size to find success, but some basic steps make a big difference:
- Make a website. Your podcast should have a basic website explaining what it’s about, introducing the host(s), and linking to episodes.
- Create social media profiles. You can use 1-2 social profiles to spread clips from your show across the web. Many mainstream podcasts became famous from having clips shared on Instagram and TikTok.
- Make a YouTube channel. You can video record your podcast episodes and upload them to YouTube for greater reach (either in part or in full). Many people prefer the visual format, so this gives your show broader appeal too.
How to Optimize Your Podcasts for Search Engines
Done right, organic search can be a powerful channel for building your audience. With Google now featuring podcasts in search results, podcast SEO can drive traffic directly to your show. Here’s how to maximize your podcast’s inbound traffic:
Perform Keyword Research:
A keyword is a word or phrase someone types into Google when searching for something online. This may seem out of place in podcasts, since you speak rather than write.
But keywords play a crucial role in podcast SEO. Google now indexes the actual conversations of your podcast and will serve them in SERPs where relevant.
This is where keyword research comes in. To appear in searches related to your podcasts, you need to include the right keywords in your content.
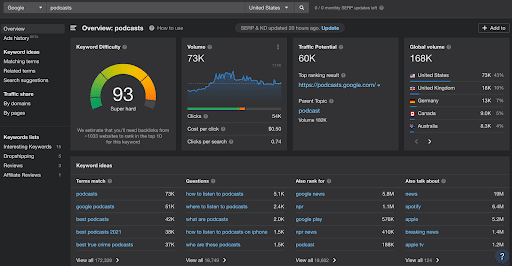
Keyword research tools are the best way to find those “right keywords.” Software like Ahrefs tells you traffic, ranking difficulty, related terms and more for any keyword.
Make a list of keywords you can realistically rank for. Then, include cover them and their parent topic in your podcast.
Build Backlinks
A backlink is a link to your podcast from another website. Search engines see each backlink as a vote of confidence in your podcast since people only link to content they find interesting.
This confidence translates into higher search rankings. So if you want to rank for competitive search terms and beat out authoritative sites, you need to build backlinks.
Upload to All Directories
A podcast directory hosts podcasts for listeners to stream and/or download. Apple Podcasts, Spotify, and iHeartRadio are examples of podcast directories.
Upload your podcast to every popular directory to get your podcasts in front of as many listeners as possible. Like how Netflix watchers can’t see Hulu content, people using Apple Podcasts can’t see your show if it’s only on Shopify.
Thankfully, you don’t have to upload your show to each directory individually. All you need to do is connect your RSS feed to each one.
Get Reviews
Every popular directly offers an internal rating system viewers can use to rate podcasts. Their internal search engines see both the star rating and the number of reviews as a huge authority signal.
In the example below, ESPN FC has almost five stars out of 2k reviews. That rating quality enables it to rank first place for “soccer podcast” in Spotify search.
You can encourage listeners to give reviews by asking them directly during the show.
Use and Optimize Images
Each episode should have cover art to make it stand out and signal what it covers. Each cover doesn’t need to be fully unique, but it should look professional to signal high quality.
Speak Slowly and Clearly
Speaking slowly and clearly is essential for three reasons:
- To make it easy for Google to understand and index your content
- So you can easily transcribe the episode with software
- So people can clearly understand what you’re saying
Listeners can speed up podcasts if they choose, so speaking too slowly isn’t an issue.
Transcribe Each Episode
While Google can index podcasts, it does better with text. Boost your SEO by transcribing your podcast and making the text publicly accessible.
Transcribing is also useful for:
- Repurposing. You can easily turn transcriptions into blog posts with some editing.
- Show notes. Let listeners skim your show’s content and skip to the parts they find interesting.
- SEO. Having your transcriptions indexed lets your podcasts appear in searches for keywords present in the text.
You don’t need to transcribe your content by hand—software can handle this for you.
Add Supporting Content
Give content to each episode with an appropriate title and description. This lets both listeners and search engines understand what your content is about.
Enable Schema
Adding schema to your podcasts allows you to become eligible to appear in Google’s rich results.
Use structured data to highlight things like episode names, descriptions, cover art, or whether your podcast contains explicit content, and other things that help Google’s crawlers understand what your show is about and who it’s for.
Before you can enable podcast schema, you’ll need to make sure that you meet all of Google’s RSS feed and Homepage requirements; otherwise, the markup features won’t appear in the SERPs.
As a quick point of reference, to appear in Google Podcasts, you’ll need to include the required podcast-level and episode-level tags, which include the following.
According to Google’s RSS feed requirements, adding relevant, recommended tags gives both searchers and search engines more information about your podcast.
The second piece of the puzzle is the Homepage requirements, which refer to a homepage specifically for the podcast, not your website’s homepage.
The homepage should clearly describe what the podcast is about and be available to Googlebot using the URL specified in your RSS feed.
Enable Google Actions
Why should you turn your podcast into a Google Action? Isn’t that for apps?
For starters, turning your podcast into an action improves your off-site presence and opens up even more opportunities to show up in the Google Search Results, in Google Podcasts, Google Play, and the Google Assistant Directory.
In May 2019, Google added a feature called Deeper Podcast search that lets users search for audio files podcasts using Google’s transcriptions.
This allows listeners to search for a specific topic covered within an episode, making it easier for users to find podcasts in the Assistant directory.
They can also play episodes directly from their phone’s mobile results, smart speaker, Google Home display, or any other device with Google Assistant installed.
How to Turn Your Podcasts into a Google Action
Creating an RSS feed for your podcast tells Google to auto-generate an Action for your show.
While you’ll need to make sure you follow the instructions to a T, once you’re set up, Google takes it from there.
Here’s what you’ll need to do to turn podcasts into Actions:
- Sign in to the Google Play Music Podcast Portal.
- Click “Add Podcast” from the menu located in the top right corner.
- Then you’ll add the RSS feed and apply required tags.
- List the required podcast tags and required episode tags.
- Follow Google’s podcast markup guidelines, then double, triple check every item is correct.
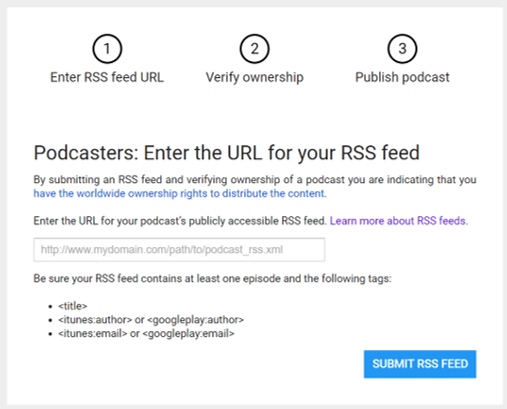
How to make your podcast into a Google Action
How to Find Podcast Guests
Featuring a guest on your podcast gives someone publicity while bringing fresh insight to your audience—a win-win for you and the guest. This guest can be an author, founder, colleague, or anyone else with authority in your field.
Many podcasters start out asking friends or colleagues to appear on their show as they build a following.
That’s all well and good, but look for some fresh voices to add to the mix:
- Search Apple Podcasts for shows with similar keywords, or browse the Apple Podcast Directory to search by category.
- Spotify and Stitcher also allow you to scroll through shows based on category and make recommendations based on listening history or what’s new.
- Search for podcasts in your niche on Google
- Browse the Google Assistant Directory. Navigate to “music and audio,” then “podcasts” and you’ll see a long list of shows you might not find on the bigger podcast channels.
- Check out other online podcast directories like cast.market for more recommendations–particularly if you’re looking for less “popular” shows.
- Outside of the “podcasting world,” head toward your usual sources to find qualified guests. Who’s in your LinkedIn network? Who have you partnered with in the past–have you hosted a conference or webinar with other thought leaders? Worked together on an industry report?
Make the opportunity appealing to the guest by doing something for them. Link to their website, feature their book, or anything else making the guest’s time worthwhile.
How to Monetize Your Podcast
Besides building recognition for your brand, podcasts can make good money. We’ll outline the best strategies for doing so here:
Sponsorships
Almost every podcaster you listen to will read through a sponsored advertisement on air. In this case, the podcaster featured a product that a sponsor deemed relevant to their audience.
While ads generate solid revenue, they usually require a larger audience with detailed demographic information. Companies need average listeners, downloads, and other listener info to know the investment will pay off.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is when someone encourages their audience to purchase a product and takes commissions for each referral. Affiliates mostly use tracking links to unique promo codes to get credit for each purchase.
Companies can invite you to their programs, or you can apply directly to them.
Either way, choose a product you’ve tried and know your audience will enjoy. You’ll lose credibility if listeners have bad experiences with products you recommend.
Wrapping Up
Podcasting offers some distinctive benefits to marketers in 2022 and beyond. It’s an engaging, personal medium, mobile-friendly, and built for today’s on-the-go, multitasking consumer.
For marketers, podcasts offer more opportunities to reach new audiences. It’s no longer just your website, social channels, and YouTube channel. It’s Apple Podcasts, Google Podcasts, Stitcher, the Assistant Directory, and if you play your cards right, a prominent place in the Featured Snippets.
As is the case with blog posts, videos, and other types of content, set it and forget it publishing won’t cut it. Again, an SEO-friendly podcast strategy depends on backlinks, optimized transcripts, and a consistent omnichannel publication plan.
As podcasts continue their meteoric rise to the top, marketers can no longer afford to ignore this opportunity.